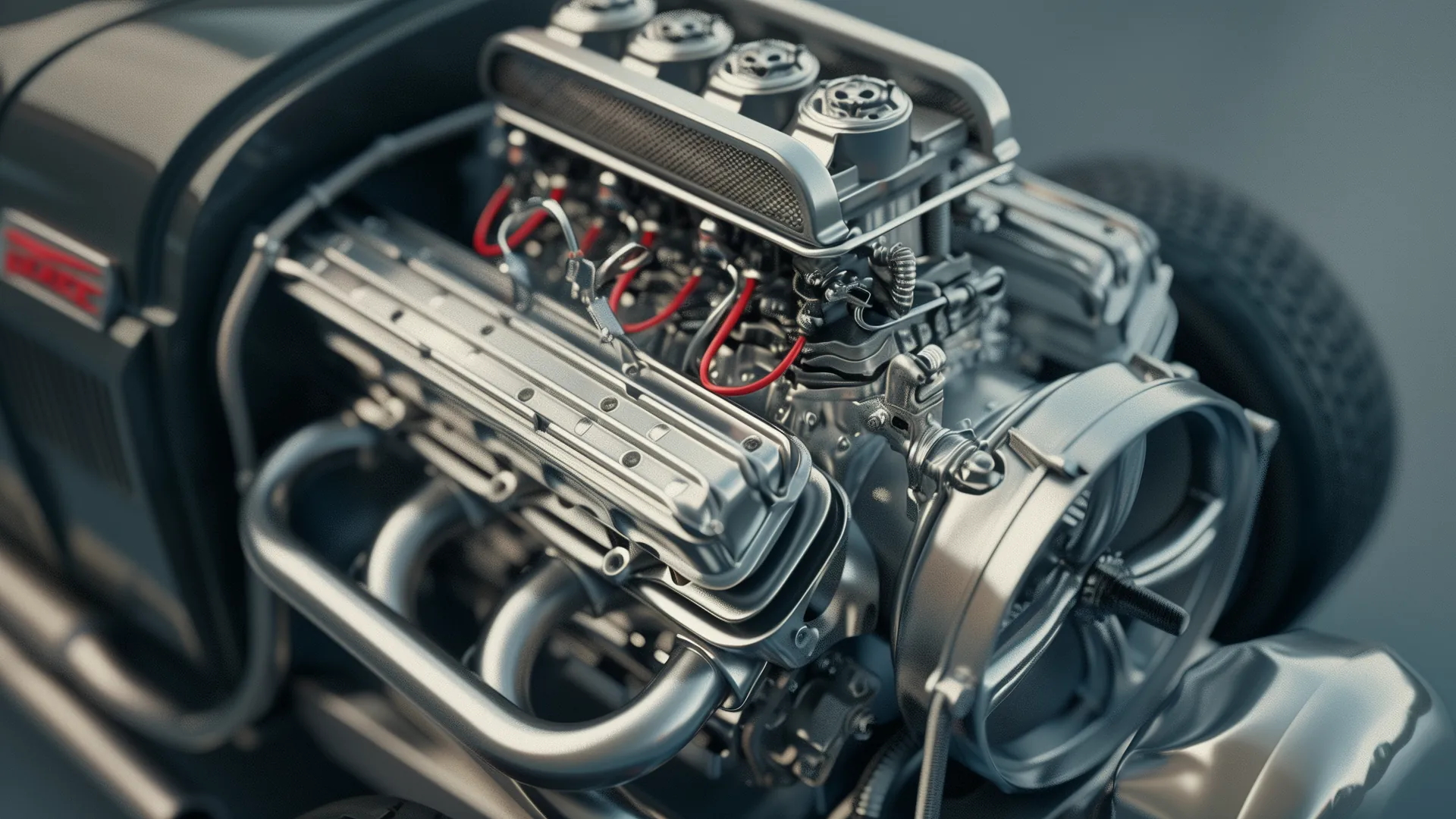
If you happen to possess an automobile or harbor a fervor for automobiles, mastering the myriad of engine types and the specialized vocabulary utilized to articulate them can prove to be a multifaceted pursuit. The engine acts as the very nucleus of any vehicle, and comprehending its inner workings will empower you to uphold your car's maintenance more competently and make judicious decisions when procuring or enhancing it. Within this introductory guide, we shall delve into the most prevalent engine types and the precise terminology employed to delineate them.
Diverse Range of Automotive Engines

Automotive engines serve as the quintessential and indispensable constituents of contemporary vehicles, furnishing them with the requisite power for locomotion. With the progression of technological breakthroughs and the swift advancement in the automotive sector, a myriad of engine types has emerged, each imbued with its own distinctive attributes, merits, and demerits. In our overview, we shall delve into the principal categories of automotive engines, encompassing gasoline, diesel, hybrid, and electric variants.
Gasoline Engines
Gasoline engines rank among the most widespread engine variants deployed in both passenger and commercial vehicles. They function by blending air with gasoline and igniting this amalgamation within the engine's cylinders through a spark engendered by spark plugs. Renowned for their elevated power output, gasoline engines offer seamless acceleration and are relatively straightforward to maintain.
Diesel Engines
Divergent from gasoline engines, diesel engines ignite fuel via the compression of air. Celebrated for their high torque output, they prove particularly efficacious for employment in trucks and buses. Diesel engines also boast high fuel efficiency, albeit often necessitating more meticulous upkeep and maintenance.
Hybrid Engines
Hybrid engines amalgamate the benefits of gasoline and electric motors. Comprising two engine types: internal combustion and electric, they facilitate diminished fuel consumption and emissions. Hybrid vehicles can harness the energy generated during braking to recharge the batteries, augmenting their energy efficiency.
Electric Motors
Vehicles propelled by electric motors utilize batteries as their energy source. They represent the most environmentally sustainable option, as they yield no deleterious gas emissions. Electric motors are also esteemed for their high energy efficiency and noiseless operation. Nevertheless, their travel range and battery charging duration are constrained.
Each enumerated type of automotive engine boasts distinctive characteristics and is apt for varied scenarios and requisites of vehicle proprietors. As technology progresses and fresh modalities of energy storage and generation come to the fore, the automotive sector continues to seek avenues to render transportation more efficient, eco-friendly, and convenient for consumers.
Automobile Engine Lexicon
Automobile engines constitute the crux of transportation. Familiarizing oneself with the rudimentary terminology associated with automobile engines not only aids car proprietors in better comprehending their vehicle's functioning but also streamlines communication with mechanics and service experts. Let us scrutinize the principal terms utilized in automotive parlance:
- Cylinder: A cylinder denotes a hollow cylindrical enclosure within the engine wherein fuel combustion transpires. A typical four-cylinder engine typically houses four cylinders, albeit the number may vary contingent upon the engine's configuration.
- Valves: Valves constitute controlled flaps that open and close synchronously with the engine's operational cycle. They regulate the influx of air and fuel into the cylinders and the discharge of exhaust gases.
- Displacement: Displacement alludes to the volume available in each cylinder for fuel combustion and air-fuel mixture. It is quantified in cubic centimeters or liters.
- Torque: Torque denotes a quantification of the force the engine generates to rotate the crankshaft. It is gauged in Newton-meters or foot-pounds.
- Compression: Compression embodies the ratio of the mixture's volume in the cylinder post-compression to its initial volume. Heightened compression augments the engine's operational efficiency.
- Fuel Delivery System: The fuel delivery system assumes responsibility for ferrying fuel to the engine's cylinders. An array of delivery systems exists, encompassing carburetors, multipoint injectors, and direct injectors.
- Ignition System: The ignition system engenders the requisite spark to ignite the air-fuel mixture in the cylinders. It encompasses spark plugs, ignition coils, and control units.
- Turbocharging: Turbocharging denotes a mechanism employed to augment the volume of the air-fuel mixture entering the cylinders by compressing the air with a turbine.
- Fuel Consumption: Fuel consumption connotes the quantum of fuel the engine consumes over a specific duration under stipulated conditions. It is quantified in miles per gallon or liters per 100 kilometers.
- Power: An engine's power signifies an indicator of its capacity to execute work. It is quantified in horsepower or kilowatts.
Apprehending the rudimentary terms pertaining to automobile engines empowers car proprietors to navigate their vehicle's operations more adeptly and interact with mechanics and service experts more efficiently.
Conclusion

In summation, automobile engines epitomize a panoply of types and specialized lexicon, each imbued with its own idiosyncratic attributes. Ranging from traditional internal combustion engines, including gasoline and diesel variants, to contemporary electric engines and hybrid systems, the choice of engine can markedly influence its performance, efficiency, and environmental footprint. Grasping these terms is imperative for anyone vested in the automotive realm, be it consumers endeavoring to make an enlightened vehicular purchase or professionals aspiring to broaden their technical acumen. As technology advances, the landscape of automobile engines continues to evolve